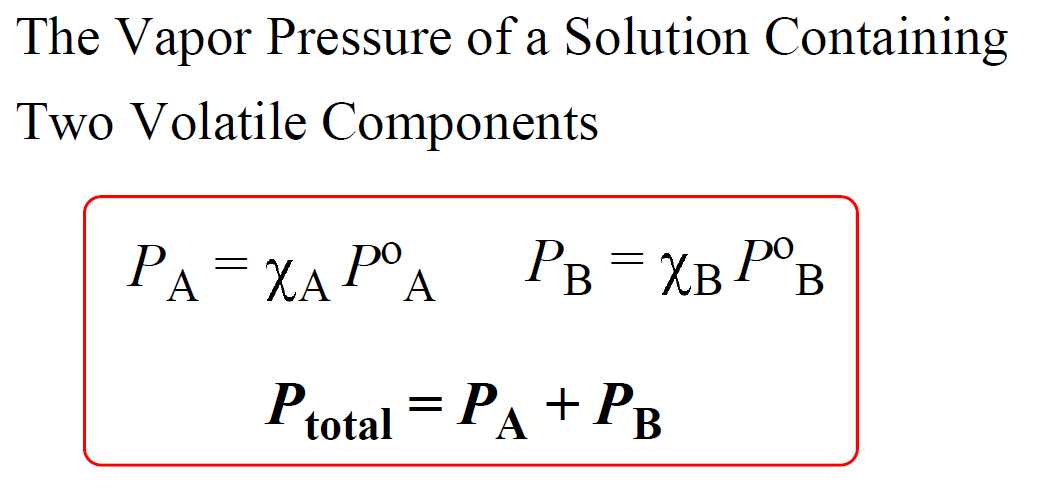What is the vapour pressure of a saturated solution of Ba(OH) 2 in an ATM? The vapor pressure of water is 23.8mmHg at 25 degrees. - Quora
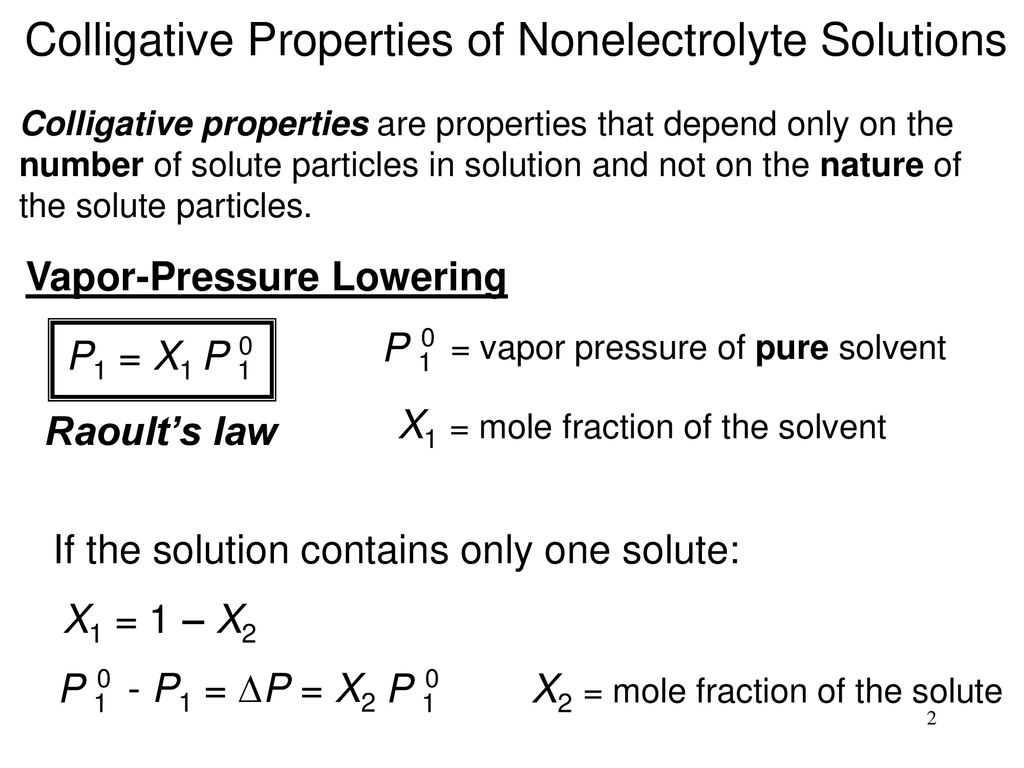
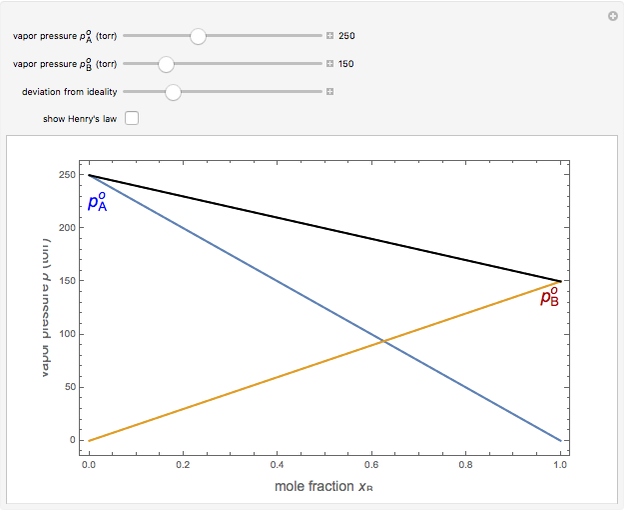
2/2/2018 OBJ: SWBAT calculate the vapor pressure with one and two solutes in the solution. What is Raoult's law and what do the variables in the equation. - ppt download
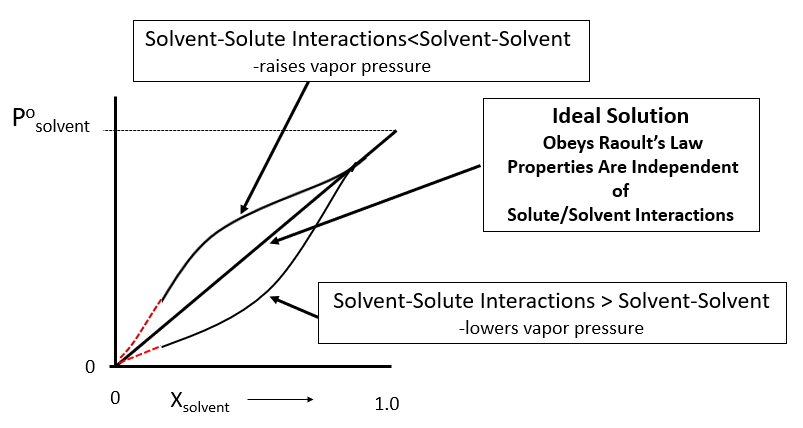
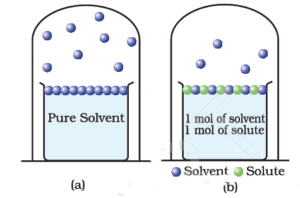
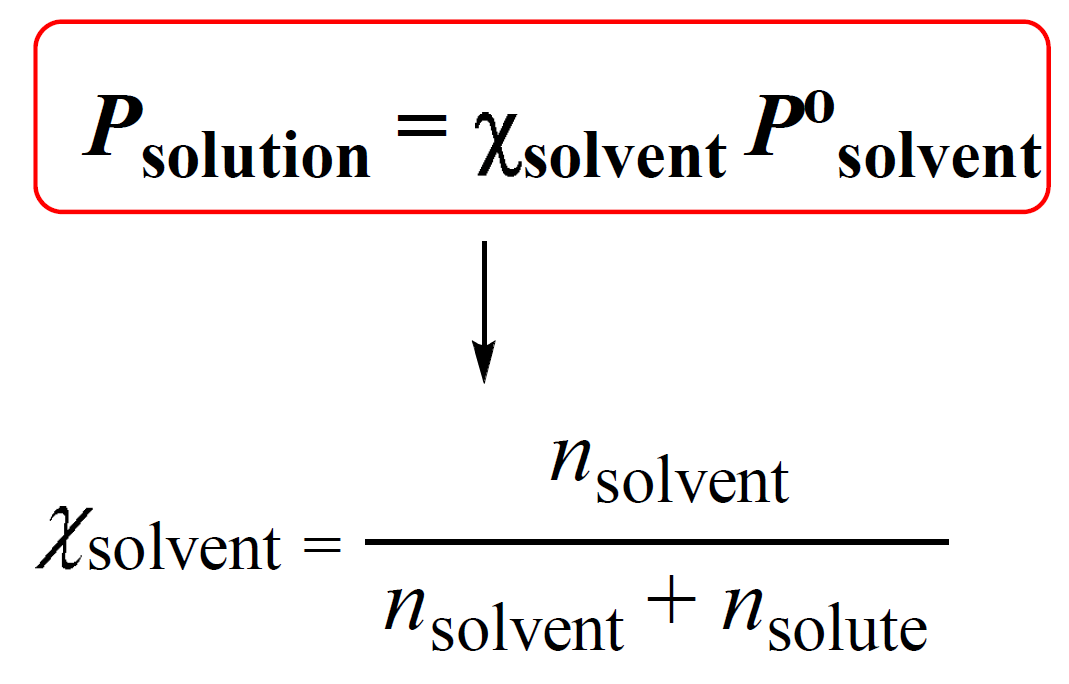
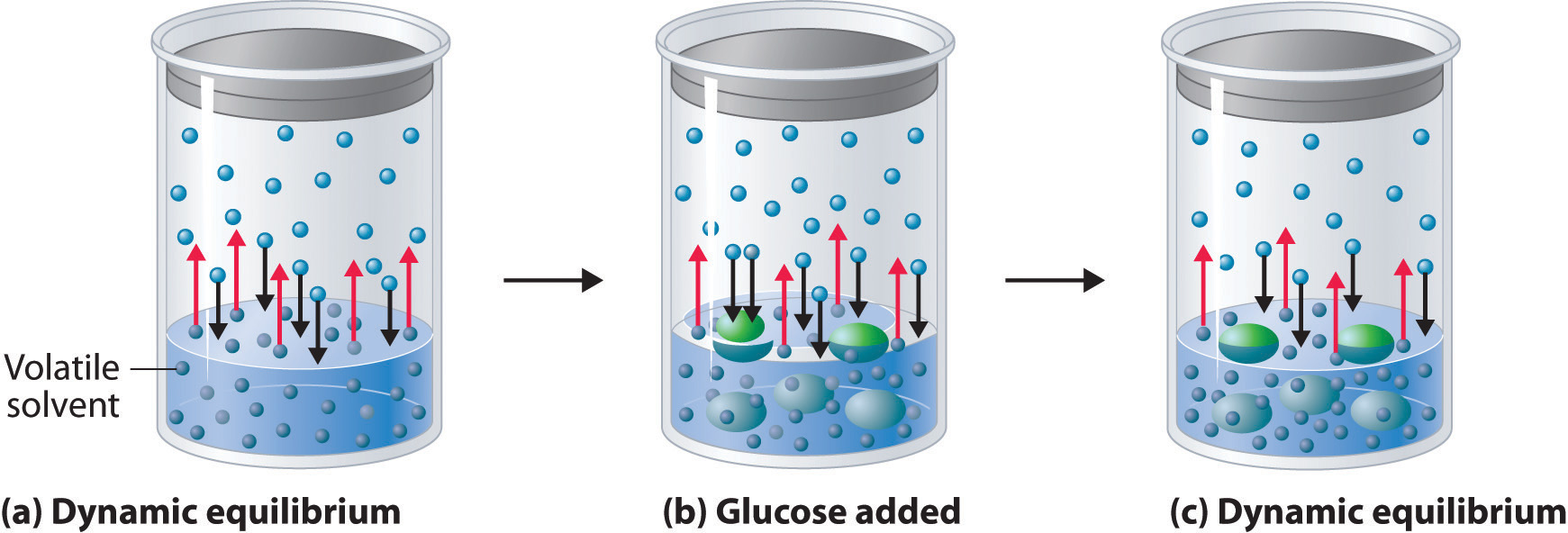
What is the reason behind the fact that the vapour pressure of a solution containing a non volatile solute is always lesser than the vapor pressure of the pure solvent? - Quora
What is the vapor pressure of a solution prepared by mixing 35.0g solid Na2SO4 (mm=142g/mol) with 175g of water at 25°C? - Quora

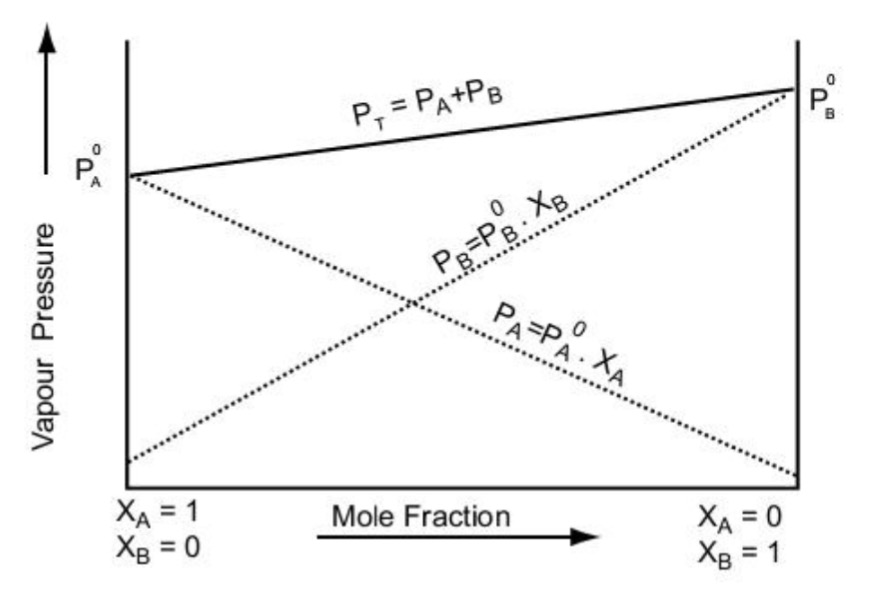
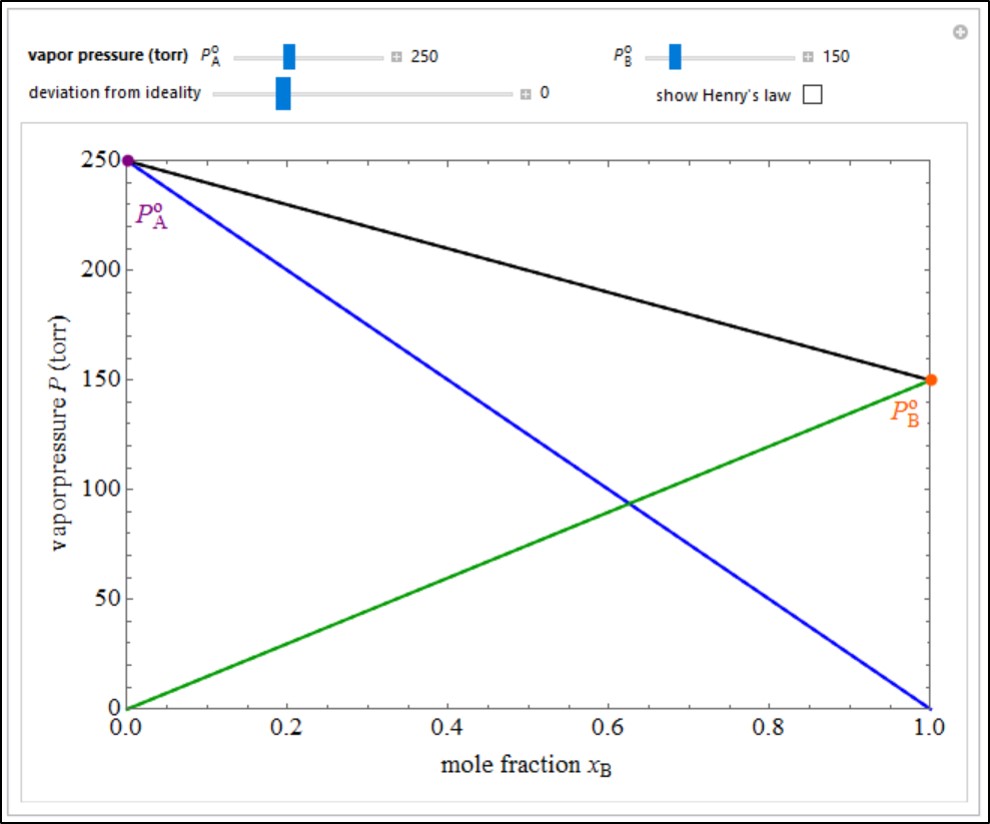
What is Vapour Pressure? - Definition, Raoult's Law, Formula with Videos & FAQs, The Vapour Pressure of Pure Liquids